The cervix is the lower, narrowing of the uterus that connects the uterus to the vagina. Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix.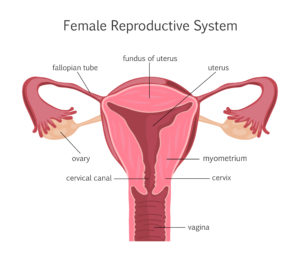
Cervical cancer is usually preventable with routine pap smears, HPV screening and the HPV Vaccine.
All women should begin having pap smears at age 21.
 Diagnosis:
Diagnosis:1. A pap smear is a test to sample cells on the surface of the cervix and screen for cervical dysplasia. HPV testing can be done at the same time. If your pap smear shows precancerous
cells, the physician may perform a colposcopy.
2. A colposcopy is a magnified exam of the cervix to detect abnormal tissue to biopsy. Sometimes an endocervical curettage is done as well and is a sampling of cells from the endocervical canal. The tissue samples are then sent to pathology for diagnosis.
3. Cone biopsy or LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure) – both are procedures under anesthesia to remove a larger amount of abnormal cervical tissue. The tissue is then sent to pathology for diagnosis.
These procedures may be done to remove precancerous cells, diagnose cervical cancer, or to treat very early stages of cervical cancer.
4. Imaging tests take pictures inside the body to see if there is a tumor. They can also show if and
how far the cancer has spread beyond the cervix. This may include an ultrasound, CT scan, PET
scan, or MRI.
